TREATMENT
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment in which sperm is directly inserted into the uterus using a small plastic catheter passed through the cervix. This procedure is typically performed at or near the time of ovulation. The sperm sample is specially prepared to select only motile and healthy sperm, which are then injected into the uterus. By bypassing the cervix, a higher number of motile sperm can reach the uterus and be available to fertilize the egg.
IUI is commonly indicated for couples with unexplained infertility, men with low sperm count or ejaculation issues, and women with ovulation disorders (in which case ovulation-stimulating medications may be prescribed). However, IUI is not suitable for cases in which both fallopian tubes are blocked or sperm quality is extremely poor.
Steps of the IUI Procedure
Initial Consultation (Day 1–3 of the Menstrual Cycle):
The woman consults with a doctor and undergoes an ultrasound. Based on her condition, the doctor selects the appropriate ovulation-stimulating medication.
Follicle Monitoring (Day 10–14 of the Menstrual Cycle):
The woman returns for an ultrasound to monitor the number and size of developing follicles and predict ovulation. If the follicles are mature, the doctor schedules the insemination and instructs the woman on how to administer an ovulation trigger injection. The male partner is advised to abstain from ejaculation for 3–5 days prior to insemination.
Insemination Day:
The male partner provides a semen sample approximately 1.5 hours before the scheduled insemination. The laboratory processes the sample, selecting only healthy, motile sperm. The woman empties her bladder and lies on an examination table similar to a gynecological exam. The sperm is then injected directly into the uterus.
Post-Insemination Rest:
The woman rests for 15 minutes at the clinic and may resume normal daily activities afterward.
Pregnancy Testing:
Approximately 14 days after insemination, if menstruation has not occurred, a urine pregnancy test is recommended. Alternatively, a blood test can be performed at the clinic.
Pre-IUI Instructions
-
The male partner should abstain from intercourse or ejaculation for 3–5 days before the scheduled insemination.
-
On the insemination day, the male partner must provide a semen sample at least 1.5 hours before the woman’s insemination.
-
Both partners should ensure adequate rest and minimize stress.
-
Avoid alcohol and smoking.
-
Refrain from using perfumes, colognes, sprays, cosmetics, or powders on the insemination day.
Post-IUI Care
-
Normal diet may be resumed immediately after the procedure.
-
Daily activities, including work and exercise, may be continued as usual.
-
Intercourse is permitted after the procedure.
-
Avoid medications that may affect pregnancy, such as certain acne treatments or antibiotics—consult your doctor if unsure.
-
Some abdominal cramping, similar to but possibly more intense than menstrual pain, may occur for several days. This is common and does not affect the success rate. Paracetamol may be used for relief.
-
Normal transportation methods, including driving, boating, flying, or riding a motorcycle, are permitted.
-
If prescribed hormonal support medications, continue taking them as instructed. Do not stop without consulting your doctor. Menstruation may be delayed; attend the scheduled pregnancy test.
-
If menstruation does not occur within 14 days of insemination or as expected, consult the clinic for a urine pregnancy test.
-
If any abnormal symptoms occur, such as vaginal bleeding or signs of allergic reactions to medication, contact the clinic immediately.
-
If the pregnancy test is positive, an ultrasound should be performed as scheduled to confirm an intrauterine pregnancy, evaluate gestational sacs, and monitor the fetal heartbeat.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483

Microfluidic Sperm Sorting
Microfluidic Sperm Sorting (MSS) is an innovative technique for selecting high-quality sperm using a specially designed device with microfluidic channels. These channels replicate the natural sperm-selection process within the female reproductive tract. Only healthy, highly motile sperm with intact DNA can navigate through the intricate channels to the opposite side of the device, while weaker or DNA-damaged sperm are unable to pass through.
Unlike conventional sperm preparation methods, microfluidic sperm sorting selects sperm based on their intrinsic characteristics without the need for centrifugation, which is known to increase DNA fragmentation.
As a result, MSS yields sperm that are highly motile, fast-moving, free from debris and reactive oxygen species (ROS), and exhibit significantly lower levels of DNA fragmentation compared with other preparation techniques. These high-quality sperm are ideal for use in IUI, IVF, or ICSI, thereby improving fertilization outcomes, embryo quality, and overall treatment success rates.

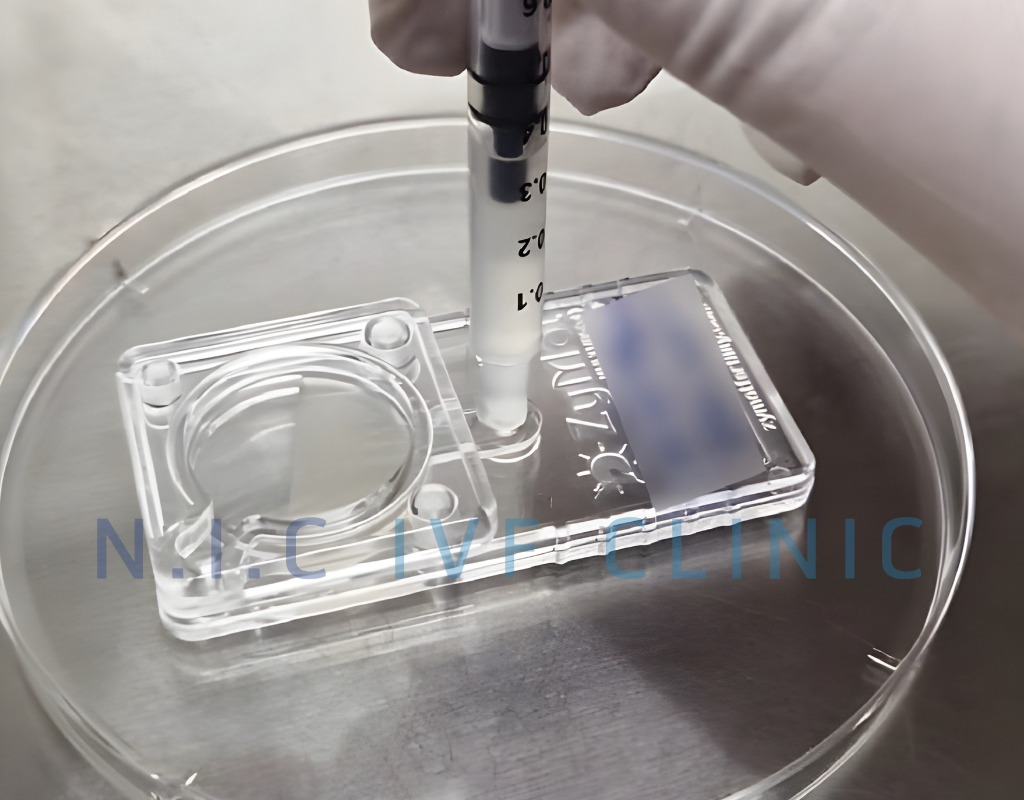
Image of Microfluidic Sperm Sorting (MSS)
Benefits of Microfluidic Sperm Sorting
-
Reduces the need for centrifugation compared with traditional methods, resulting in lower sperm DNA fragmentation.
-
Minimizes the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage sperm.
-
Mimics natural selection, allowing only motile, morphologically normal sperm capable of fertilization to pass through.
-
Provides high-quality sperm suitable for fertilization, thereby increasing the chances of success in IVF or ICSI.
Who Can Benefit from Microfluidic Sperm Sorting?
-
Men with high levels of sperm DNA fragmentation.
-
Men experiencing male-factor infertility or poor semen quality.
-
Individuals seeking to reduce ROS exposure or avoid centrifugation.
-
Couples who have previously undergone IVF or ICSI without success.
-
Couples aiming to improve embryo quality and increase pregnancy rates.
Article by
Ms. Piyarat Sophaboon, M.Sc., Embryologist
For more information, please contact us via:
LINE Official : @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483
IVF / ICSI
IVF Procedure
-
Ovarian Stimulation
The female patient visits the physician within the first 1–3 days of the menstrual cycle for an ultrasound and hormonal evaluation. Based on the results, the physician will prescribe ovarian stimulation medications tailored to the individual.
After starting ovulation stimulation injections, the woman will have 2–3 monitoring ultrasounds, depending on the growth rate of the follicles. When the eggs reach full maturity (usually larger than 17–18 millimeters), the physician will schedule the ovulation trigger injection and advise the male partner to abstain from ejaculation for 3–5 days prior to the scheduled egg retrieval.
-
Egg Retrieval Day
On the day of egg retrieval, the male partner provides a semen sample. Egg retrieval is performed under intravenous sedation.
Fertilization is typically carried out using Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), in which a single sperm is injected directly into each egg. The resulting embryos are cultured until they reach the blastocyst stage.
For fresh embryo transfer, embryos are transferred to the uterus 3–5 days after egg retrieval. If the physician recommends freezing the embryos for a later cycle, the female patient will return on days 1–2 of the next menstrual cycle for ultrasound and uterine lining preparation with medications.
Pregnancy Testing: A blood test for pregnancy hormones (β-hCG) is performed 7–10 days after embryo transfer.
Egg Retrieval Procedure
Egg retrieval is a critical step in the IVF process and is performed approximately 34–36 hours after the ovulation trigger injection. Eggs are collected transvaginally using a fine needle attached to an ultrasound probe, allowing identification and aspiration of the follicles. The procedure is performed under intravenous sedation and typically takes less than 30 minutes. The aspirated follicular fluid is then examined by an embryologist to assess egg quality and select suitable eggs for ICSI.
Pre-Egg Retrieval Instructions
-
Confirm and adhere strictly to the scheduled date and time for the ovulation trigger injection.
-
Do not eat or drink for at least 8 hours before the procedure.
-
Arrive at N.I.C IVF Clinic at least 1 hour prior to the procedure for preparation.
-
Cleanse the body and genital area before the procedure.
-
The male partner should be prepared to provide a semen sample at the same time as egg retrieval.
-
Abstain from sexual intercourse, as it may affect the ovaries.
-
Avoid scented products, including perfumes, sprays, cosmetics, or powders on the day of egg retrieval.
-
Remove nail polish before the procedure.
-
Do not wear jewelry or bring valuables to the clinic.
Post-Egg Retrieval Care Instructions
-
Mild nausea, abdominal discomfort, or light vaginal bleeding may occur upon waking from sedation.
-
Rest in the recovery room for approximately 1–2 hours before going home.
-
Pain relief medication may be taken as prescribed.
-
Strictly follow the physician’s instructions regarding all medications (injections, oral, or suppositories).
-
Prioritize rest and maintain a positive emotional state.
-
Do not drive yourself home; it is essential to be accompanied by a relative or companion.
-
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe bloating, intense abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, significant abdominal enlargement, or abnormal vaginal bleeding.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483

PGT-A / NGS
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Technology
The technology of preimplantation genetic testing has advanced significantly in recent years. Originally developed in 1980, this testing relied on Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to amplify genetic material, primarily focusing on sex-linked chromosomal disorders. Due to technical limitations at that time, the testing could only determine the sex of the embryo and could not identify specific gene or chromosomal abnormalities. Consequently, embryos were often selected based solely on sex to avoid severe genetic diseases. This approach sometimes resulted in the discarding of embryos of the opposite sex that may have been healthy or only mild carriers, without knowledge of their actual genetic condition. This limitation highlighted the need for more specific techniques capable of identifying both the sex and the presence of genetic or chromosomal abnormalities.
Over time, significant advancements have been made in both genetic amplification and diagnostic accuracy. Techniques such as Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH), Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), real-time PCR, and Karyomapping have been developed. Currently, the most widely used technology for preimplantation genetic testing prior to embryo transfer is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS).
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) is a modern base-by-base sequencing technology that enables rapid and comprehensive analysis. It allows for the assessment of all 24 chromosomes of an embryo in a single test, as illustrated in Figures 1 and 2. NGS offers a high accuracy rate of up to 95–97%. Since current testing is performed at the blastocyst stage, where more cells are available for analysis, the precision of the test is further enhanced.
In addition to detecting whole-chromosome aneuploidy (gain or loss of entire chromosomes), NGS can identify segmental aneuploidy, which refers to partial chromosomal abnormalities. Older techniques, such as FISH or CGH, are unable to detect these segmental changes. Moreover, NGS has been shown to improve pregnancy success rates and reduce miscarriage rates by up to 50%, representing a crucial advancement in reproductive genetics.
Picture 1 demonstrates female embryo with normal chromosomes using NGS method: 46 XX.
Picture 2 demonstrates male embryo with normal chromosome using NGS method: 46 XY.

By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483
EGG FREEZING
In modern Thai society, there is a growing trend of marrying at an older age. As is well known, maternal age has a direct impact on the quality of a woman’s eggs. As illustrated in Figure 1, the most fertile age range is between 25 and 29 years. After this period, fertility gradually declines, with a marked decrease occurring after the age of 35. This decline in fertility forms the basis for the recommendation to consider egg freezing before the age of 35. Egg freezing preserves the age and quality of the eggs at the time of retrieval, thereby preventing further deterioration as the woman ages.
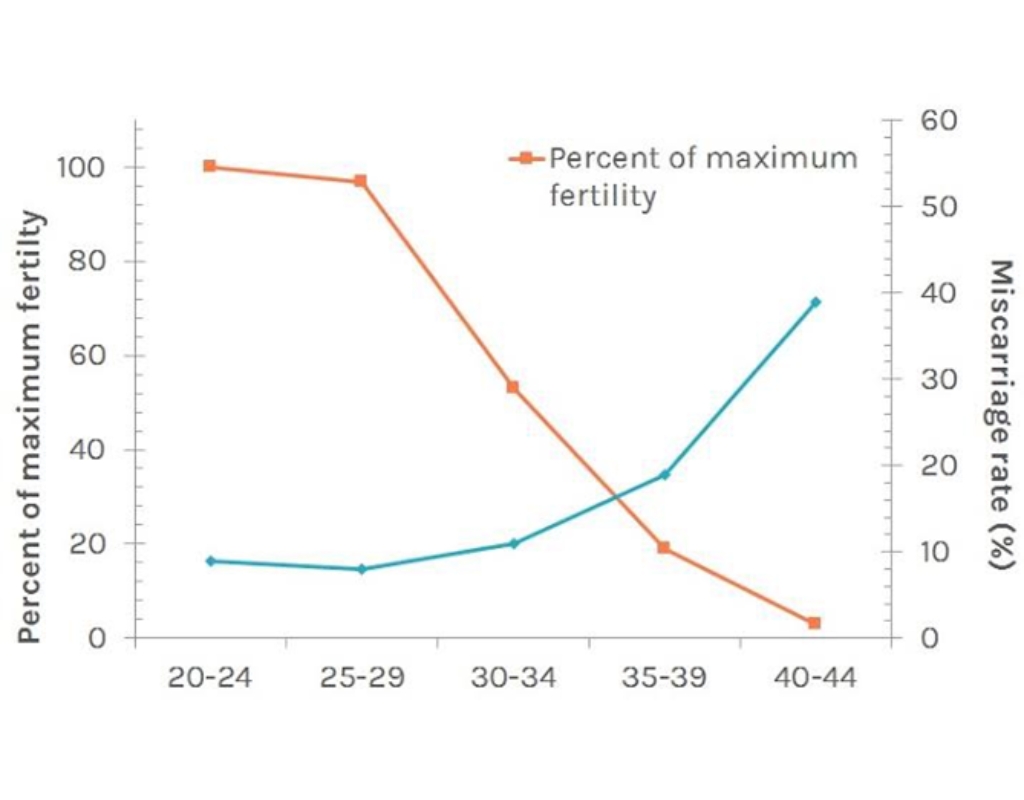
Picture 1 demonstrates the relationship between ages and reproductive percentile.
Additionally, eggs from women over 35 years of age are more likely to result in embryos with chromosomal abnormalities when fertilized with sperm. This is illustrated in Figure 2.
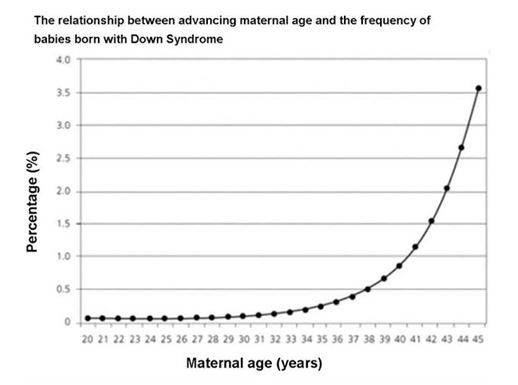
Picture 2 demonstrates the relationship between age of women and percentile of having Down syndrome babies.
Moreover, a woman’s egg supply is determined before birth, with the highest number of eggs present at around seven months of gestation. From that point onward, the number of eggs gradually declines over time. This natural age-related decline is the reason why it is advisable to consider egg freezing at a younger age, as illustrated in Figure 3.

Oocyte Freezing Process
The process of oocyte freezing involves stimulating the ovaries with hormone injections, following a protocol similar to that used in in vitro fertilization (IVF), to retrieve a sufficient number of mature eggs. Once the eggs have reached the appropriate stage of maturity, they are collected from the body and frozen prior to fertilization with sperm.
The freezing technique is essentially the same as that used for embryo cryopreservation, with the primary difference being the type of cryoprotective agents employed. However, frozen oocytes tend to be less robust than frozen embryos. Upon thawing for fertilization, approximately 80% of the frozen eggs are expected to survive the process.
Indications for Oocyte Freezing
-
Elective egg freezing: For the purpose of future fertilization with a legally married partner’s sperm.
-
Medical egg freezing: For women diagnosed with certain cancers who will undergo treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery that may impair ovarian function. Egg freezing may also be considered for other medical conditions where treatment is expected to adversely affect the quantity or quality of oocytes in the future.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483
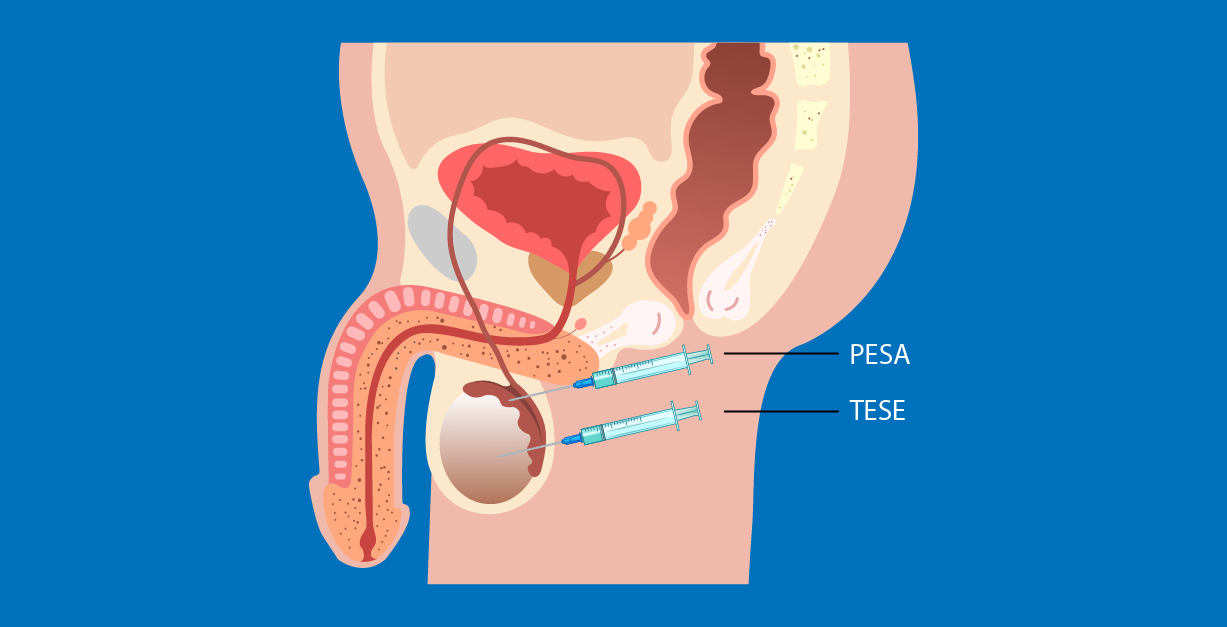
Testicular Sperm Retrieval: PESA/TESE Techniques
Testicular sperm retrieval is indicated in cases where the male partner is diagnosed with specific reproductive disorders. The procedure may be considered in the following situations:
- The semen sample contains no sperm (azoospermia) due to obstruction of the spermatic ducts or congenital absence of the vas deferens.
- Natural ejaculation is not possible.
- The patient experiences ejaculatory dysfunction due to spinal cord injury or other health-related issues, or when ejaculated sperm are all non-viable.
- The patient has undergone vasectomy and does not wish to undergo vasectomy reversal.
In the past, men diagnosed with such conditions were unable to have biological children unless donor sperm was used. However, with advances in medical technology, it is now possible for men with obstructive or non-obstructive azoospermia where spermatogenesis still occurs in the testes to father their own children. This is made possible through surgical sperm retrieval techniques that allow sperm to be obtained directly from the site of production the testis. This method increases the chances of retrieving viable sperm suitable for use in assisted reproductive technologies, such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Surgical sperm retrieval can be performed as long as the testes are capable of producing sperm. The specific technique chosen is based on clinical evaluation and at the discretion of the physician. The two primary methods of testicular sperm retrieval are
- PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration): A minimally invasive procedure in which a fine needle is used to aspirate sperm from the epididymis.
- TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction): A minor surgical procedure in which a small sample of testicular tissue is removed for examination and extraction of sperm.
Each method has its indications depending on the underlying cause of male infertility, and a reproductive specialist will determine the most appropriate approach based on individual diagnosis and clinical context.
PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration)
PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration) is a minimally invasive technique for sperm retrieval that involves the use of a fine needle, approximately 2 millimeters in diameter, to aspirate fluid from the epididymis. The epididymis, located at the upper part of the testicle, is where sperm cells are collected and stored after being produced in the seminiferous tubules.
During the procedure, a needle is carefully inserted into the epididymal region to aspirate fluid containing spermatozoa. The retrieved fluid is then examined under a microscope to identify the presence of sperm and assess sperm quality for potential use in assisted reproductive techniques.
The PESA procedure typically takes approximately 10 to 20 minutes to complete. It can be performed under local anesthesia or intravenous sedation, depending on patient preference and medical evaluation. After the procedure, the patient is usually observed for about one hour and may return home the same day without the need for extended hospitalization.

TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction)
In cases where no spermatozoa are retrieved through aspiration from the epididymal ducts, the TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction) procedure may be performed. This technique involves making a small incision, approximately 1–2 millimeters in size, in the scrotal skin to access the testicular tissue directly.
A small biopsy of testicular tissue is surgically obtained from areas likely to contain active spermatogenesis. The tissue is then processed and examined under a microscope to identify the presence of viable sperm for use in assisted reproductive techniques such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
TESE is typically performed under intravenous sedation or general anesthesia. Postoperative discomfort is generally mild and can be managed with oral analgesics. Most patients report a significant reduction in pain within three days following the procedure.

Guidelines Before the Procedure
Prior to testicular sperm retrieval, the physician will require a blood test to evaluate overall health and assess surgical fitness. Patients must abstain from eating and drinking for at least 6–8 hours before the procedure, in accordance with standard preoperative protocols.
Preoperative Instructions for Testicular Sperm Retrieval
-
Undergo all required preoperative blood tests as advised by the physician.
-
Fast from both food and water for at least 6–8 hours prior to the procedure.
Postoperative Care Instructions
-
Wound care: Keep the incision dry. Avoid getting the wound wet, and refrain from swimming or soaking in a bathtub until fully healed.
-
Hygiene: After urination, gently pat the area dry to maintain a clean and dry wound.
-
Medications: Take all prescribed analgesics and antibiotics as directed to reduce pain, swelling, and the risk of infection.
-
Physical activity: Avoid strenuous exercise and heavy physical activity for at least two weeks to prevent testicular pain or swelling.
-
Sexual activity: Refrain from sexual intercourse until the wound is completely healed.
Potential Complications
Although rare (occurring in fewer than 2% of cases), postoperative complications may include:
-
Infection
-
Hematoma (accumulation of blood within the testicle)
-
Postoperative pain at the surgical site
These complications are generally mild and can be effectively managed with appropriate medical care.
Success Rates of Testicular Sperm Retrieval
Testicular sperm retrieval procedures have demonstrated high success rates, particularly in patients with obstructive azoospermia. Outcomes depend on the underlying cause of infertility, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of viable sperm within the testicular tissue.
Safety of PESA and TESE Procedures
PESA and TESE are considered safe and minimally invasive procedures. They provide additional treatment options for couples experiencing male-factor infertility. Current evidence indicates that these procedures do not increase the risk of congenital anomalies or developmental disorders in offspring compared to the general population.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483
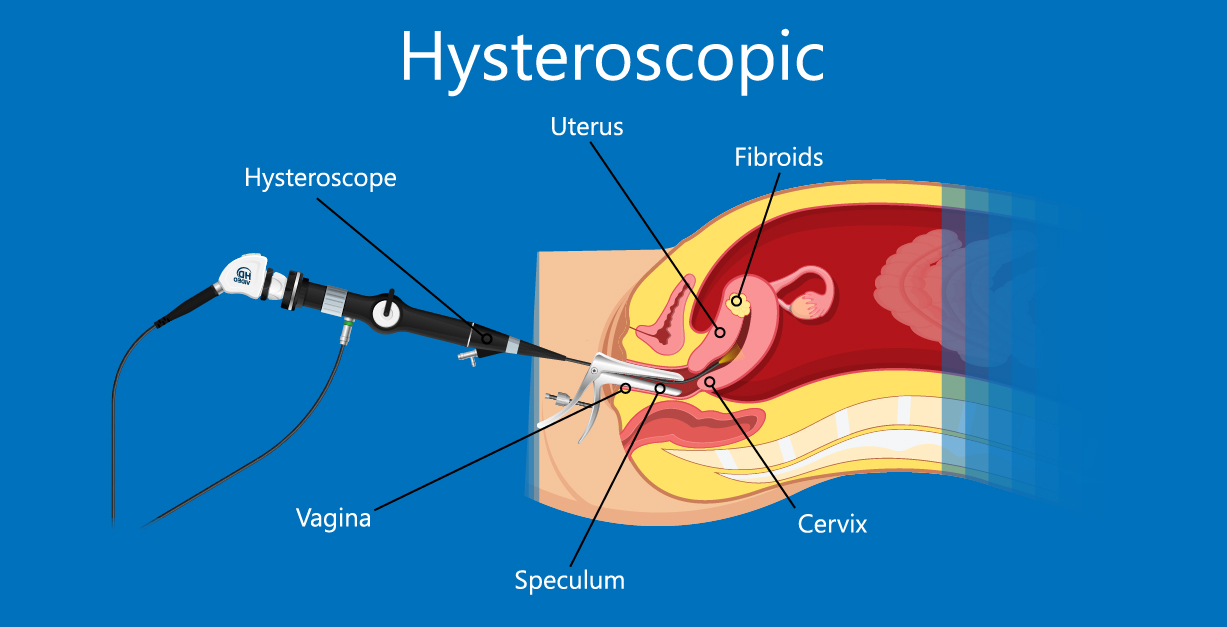
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopic Surgery in Uterine Cavity for Infertility Patients
In some patients, pregnancy may not occur even when embryos have normal chromosomes and routine evaluations show no obvious problems. In these cases, implantation failure may be suspected. Patients are often advised to have their uterine cavity examined, even if they do not have symptoms. Common symptoms that may indicate uterine issues include heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding and menstrual pain.
Hysteroscopy is a widely used method to evaluate the uterine cavity. It allows doctors to both diagnose and treat any abnormalities. There are generally two types of hysteroscopic procedures:
1. Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is a minor procedure that can be performed in the outpatient clinic. A small hysteroscope, usually 2.9–4 millimeters in diameter, is inserted into the uterine cavity to examine its structure.
-
Normal endometrium: A healthy uterine cavity with no fibroids or polyps that could interfere with embryo implantation. The lining is smooth and uniform, as shown in Picture 1.
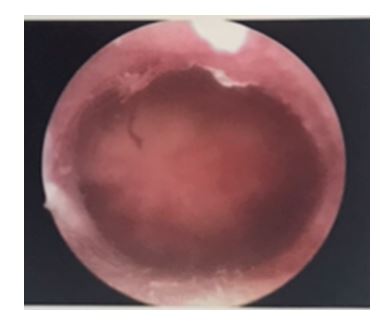
Picture 1 demonstrates a normal uterine cavity from performing diagnostic hysteroscopy.
- Endometrial Polyps and IVF
Endometrial polyps are small growths in the lining of the uterus that are commonly found in an abnormal uterine cavity. They often do not cause any symptoms. Small polyps may be expelled naturally during menstrual bleeding, and they are typically noncancerous.
However, even after removal, polyps can recur. It is important to treat endometrial polyps before attempting embryo transfer, as they can interfere with implantation and reduce the chances of pregnancy (as shown in Picture 2).

Picture 2 demonstrates endometrial polyp inside the uterine cavity.
-
Submucous Myoma and IVF
Submucous myomas are fibroids commonly found in women of reproductive age. When they develop inside the uterine cavity, they can interfere with pregnancy. As shown in Picture 3, they may cause no symptoms or may lead to heavy menstrual bleeding, which can result in anemia.
Although these fibroids are usually noncancerous, they should be removed before pregnancy to improve the chances of successful embryo implantation.

Picture 3 demonstrates fibroid that grows inside the uterine cavity.
- Septate Uterus and IVF
A septate uterus is a congenital uterine abnormality in which the inner portion of the uterine cavity is divided by a band of tissue. This can prevent embryo implantation or increase the risk of miscarriage.
The condition can be treated surgically by removing the dividing tissue in the uterine cavity, as shown in Picture 4, to improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.

Picture 4 demonstrates the surgery to remove a wall of tissue inside the uterine cavity.
- Uterine Synechiae and IVF
Uterine synechiae, also known as intrauterine adhesions, usually occur after a dilatation and curettage (D&C) procedure or following a severe infection in the uterine cavity. These adhesions can interfere with embryo implantation and reduce the chances of pregnancy.
Surgical treatment is recommended to remove the adhesions before attempting pregnancy, improving the likelihood of a successful implantation.
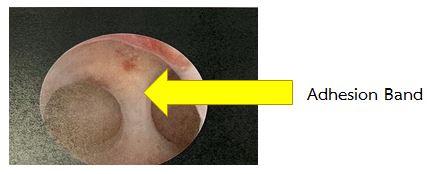
Picture 5 demonstrates adhesion band inside the uterine cavity.
2. Hysteroscopic surgery
Hysteroscopic surgery is performed in the operating room. Usually, a larger hysteroscope is used compared to diagnostic hysteroscopy, and the cervix may need to be gently dilated before inserting the camera. Additional instruments such as electric loops, small scissors, or a morcellator may be used to remove polyps, fibroids, adhesions, or septa inside the uterine cavity. Patients may receive medication to help them relax and minimize discomfort during the procedure.
The optimal time for diagnostic hysteroscopy or hysteroscopic surgery is after the menstrual period and before ovulation. During this period, the uterine lining is thin and not swollen, allowing clear visualization of any pathology.
Preparation for Hysteroscopy
1. Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
-
This procedure is usually performed in the outpatient department (OPD) without anesthesia.
-
Fasting is generally not required, but avoid eating 2–3 hours before the procedure to reduce the risk of nausea.
-
Use the restroom beforehand and you may take mild pain relief medication about an hour prior to the procedure.
2. Hysteroscopic Surgery
-
Fast for 6–8 hours before surgery.
-
Vaginal medication may be administered 6–8 hours before surgery to help dilate the cervix and facilitate the procedure. Mild side effects, such as low-grade fever, abdominal discomfort, or light vaginal bleeding, may occur but typically resolve after surgery.
Post-Surgery Instructions
-
Complete the full course of prescribed antibiotics.
-
Avoid sexual intercourse, swimming, and strenuous exercise for 2 weeks.
-
Maintain a healthy diet; there are no specific dietary restrictions.
-
Light vaginal bleeding may occur for up to a week and is usually odorless. Mild cramping similar to menstrual pain is common and not harmful.
-
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe pain, heavy bleeding, fever, or any unusual symptoms.
By Doctor Warawun Lupthalug
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483

Specialized Techniques
Our clinic offers a range of advanced technologies specifically designed to improve success rates and outcomes in assisted reproductive procedures. These specialized techniques include:
-
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
NGS is a cutting-edge method for comprehensive chromosomal screening of embryos. Unlike older techniques such as Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH), which can detect only 5 chromosome pairs, NGS can analyze all 24 chromosomes (23 pairs + sex chromosomes). This advanced technology increases the accuracy of embryo selection, reduces miscarriage rates, and significantly improves the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy by ensuring that only chromosomally normal embryos are transferred. -
MACS® ART Annexin V System
This technology removes apoptotic (non-viable or dying) sperm prior to fertilization. By filtering out non-viable sperm, the remaining sperm have higher viability and genetic integrity, which has been shown to increase fertilization and pregnancy rates compared to conventional sperm preparation methods. -
Halosperm® G2
Halosperm G2 is a diagnostic assay used to detect sperm DNA fragmentation. This method enables embryologists to select sperm with intact DNA for fertilization. Improved sperm DNA integrity has been linked to higher fertilization rates, better embryo development, and improved implantation potential. -
Endometrial Receptivity Test (ERA®)
ERA is a personalized diagnostic tool that determines the optimal implantation window for each woman. Since endometrial receptivity timing varies individually, this test provides a customized recommendation for precise embryo transfer timing. Clinical studies show that ERA-guided transfers improve implantation and pregnancy rates in women with repeated implantation failure or unexplained infertility. -
Oosight® Spindle Imaging System
Oosight is a high-resolution polarized light microscope that allows visualization of the meiotic spindle in oocytes during ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection). This allows embryologists to avoid structural damage to the oocyte during injection, resulting in higher fertilization rates and improved embryo development compared to conventional ICSI performed without spindle imaging. -
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic Disease (PGT-M)
PGT-M is a specialized genetic screening to identify single-gene disorders in embryos, particularly for couples with known hereditary risks. Common conditions include:
-
Thalassemia
-
Hemophilia
-
Huntington’s disease
-
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
-
Other inheritable monogenic disorders
This testing requires expert knowledge in reproductive genetics. Our team includes Assoc. Prof. Dr. Matchuporn Sukprasert, Thailand’s first specialist in this field trained at Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University, New York, USA. Her expertise ensures precise diagnosis, appropriate counseling, and optimal embryo selection for families at risk of genetic disorders.
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483
Embryo Transfer (ET)
Embryo Transfer (ET)
Embryo transfer is the final step in assisted reproductive technology. Although it can be the most anxiety-inducing part for patients, the procedure is similar to a routine gynecological pelvic exam—only gentler. It is performed painlessly to prevent uterine contractions, so sedation or pain relief is generally unnecessary.
During the procedure, a small, soft plastic catheter is inserted into the uterine cavity, and the embryo is placed at the optimal location. Abdominal ultrasound guidance is typically used to ensure precise placement and maximize the chances of pregnancy.
Patient Instructions Before Embryo Transfer (ET)
-
Please check in with the staff on the scheduled date and before your appointed time as instructed by the doctor to prepare for the procedure.
-
Shower and maintain personal hygiene.
-
Fasting is not required; you may eat and drink normally.
-
Avoid scented products such as perfumes, sprays, cosmetics, or body powders.
-
Do not wear jewelry or bring valuables on the day of the procedure.
Vaginal Medication Instructions
-
If your appointment is before noon, do not apply vaginal medication that morning.
-
If your appointment is after noon, continue using vaginal medication as prescribed.
Patient Instructions After Embryo Transfer (ET)
-
Remain lying down for at least 30 minutes immediately after the procedure.
-
Rest at the clinic for at least 1 hour before going home.
-
Resume eating normally, preferably light, easily digestible food.
-
Follow all prescribed medications (injectable, vaginal, or oral) carefully.
-
Avoid sexual intercourse for approximately 14 days or until the scheduled blood test.
-
Do not douche or insert anything into the vagina.
-
Avoid lifting heavy objects or engaging in intense physical activity (e.g., workouts, hot yoga, sauna).
-
Manage diet to prevent constipation or diarrhea.
-
Avoid crowded places and shared swimming pools to reduce the risk of infection.
-
Get adequate rest; lying on your back or side is sufficient—bed rest all day is not required, but avoid sudden or vigorous movements.
-
Do not drive yourself to prevent sudden jolts or impacts.
-
Return for a blood test to check for pregnancy approximately 7–14 days after the procedure.
-
Contact doctor immediately if you experience unusual bleeding, lower abdominal pain, or abnormal vaginal discharge.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483

Endometrial Receptivity Test (ERA® Test)
ERA® Test is a diagnostic technology that identifies the most suitable time for the endometrium to allow embryo implantation. The optimal implantation window can vary from person to person. This test helps determine the ideal timing for embryo transfer, improving implantation success and overall pregnancy rates.
ERA® Test uses Microarray technology to analyze endometrial tissue. It identifies the specific stage of the menstrual cycle when the endometrium is most receptive to embryo implantation.
Who is the ERA® Test Suitable For?
-
Patients who have had multiple transfers of good-quality embryos but have not achieved pregnancy.
-
Patients with repeated miscarriages.
-
Patients with a history of difficult endometrial preparation.
-
Patients with a limited number of embryos available for transfer.
How is the ERA® Test Performed?
-
Endometrial Preparation: The doctor administers medications to prepare the endometrium and monitors its thickness via ultrasound.
-
Endometrial Biopsy: A tissue sample is collected from the endometrium.
-
Analysis: The sample is analyzed to determine the personalized implantation window.
-
Results: Analysis usually takes about 1 month.
-
Embryo Transfer: The embryo transfer is scheduled according to the optimal timing identified by the ERA® Test.
Benefits of the ERA® Test
-
Identifies the personalized implantation window for each patient.
-
Increases the likelihood of successful embryo implantation.
-
Improves pregnancy rates, especially for patients with repeated implantation failures.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
.
If you’d like to learn more, we’re always here to help:
Line@: @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483

SAGE 1-Step™ GM-CSF
What is SAGE 1-Step™ GM-CSF?
SAGE 1-Step™ GM-CSF is an embryo culture medium specifically designed for use after embryo warming. It is developed based on the widely used SAGE 1-Step™ medium, which has long been established in embryo culture systems.
SAGE 1-Step™ GM-CSF represents a new standard in embryo culture and embryo transfer media. It is enriched with key components, including Hyaluronan and GM-CSF (Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor). These components help create an optimal environment for embryo development, reduce cellular stress, decrease embryo apoptosis, and increase the likelihood of successful implantation.
Why Choose SAGE 1-Step™ GM-CSF?
-
Single-Step Medium
Allows continuous embryo culture until the day of transfer without the need to change media, helping to minimize embryo stress.
-
GM-CSF Supplementation
GM-CSF is an important protein that supports communication between the embryo and the endometrium, enhances implantation potential, and reduces embryo cell death (apoptosis).
-
Suitable for Both Culture and Transfer
Can be used throughout embryo culture and during embryo transfer procedures (Culture & Transfer).
Clinical Benefits of GM-CSF
-
Enhances communication between the embryo and the endometrium
-
Supports efficient embryo development
-
Protects embryos from cellular stress and reduces apoptosis
-
Increases implantation potential
-
Supports appropriate immune modulation for implantation
-
Promotes ongoing pregnancy
-
Improves overall pregnancy success rates
An Advanced Treatment Option
SAGE 1-Step™ GM-CSF is an advanced option for both embryo culture and embryo transfer, supporting optimal conditions throughout the treatment process.
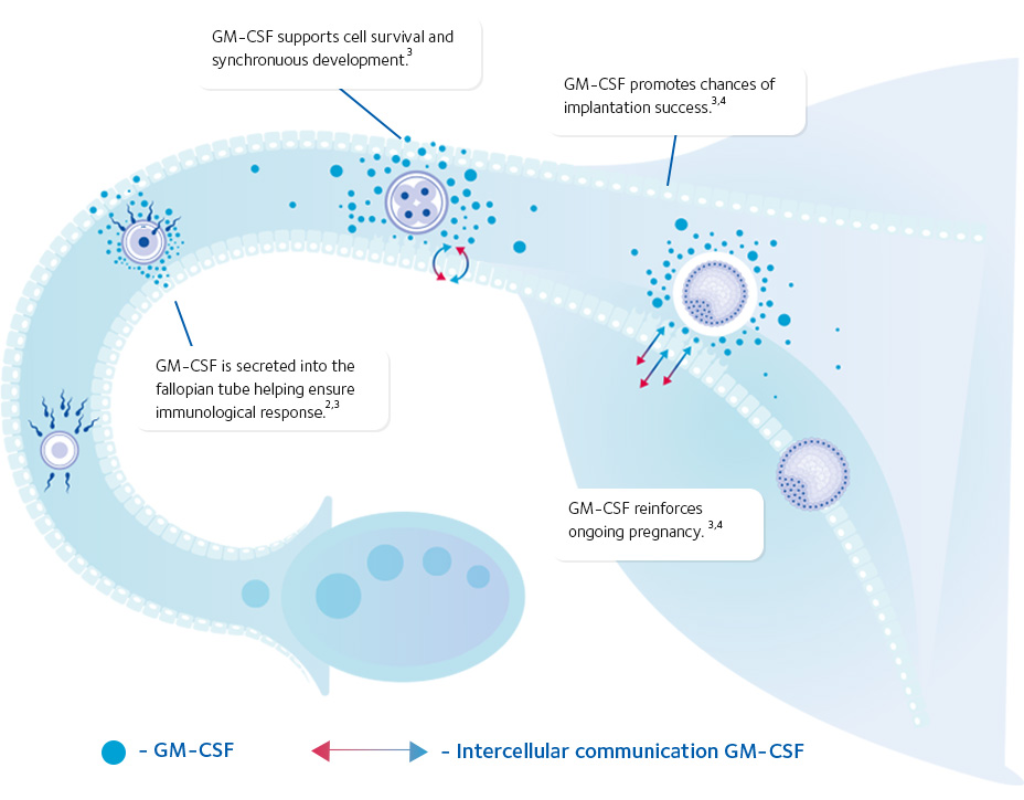
Scientific Evidence Supporting GM-CSF
-
Embryos cultured in SAGE 1-Step™ GM-CSF demonstrate improved morphological quality, including reduced fragmentation and blastomere inequality
-
Higher implantation rates and improved ongoing pregnancy rates compared with conventional embryo culture media
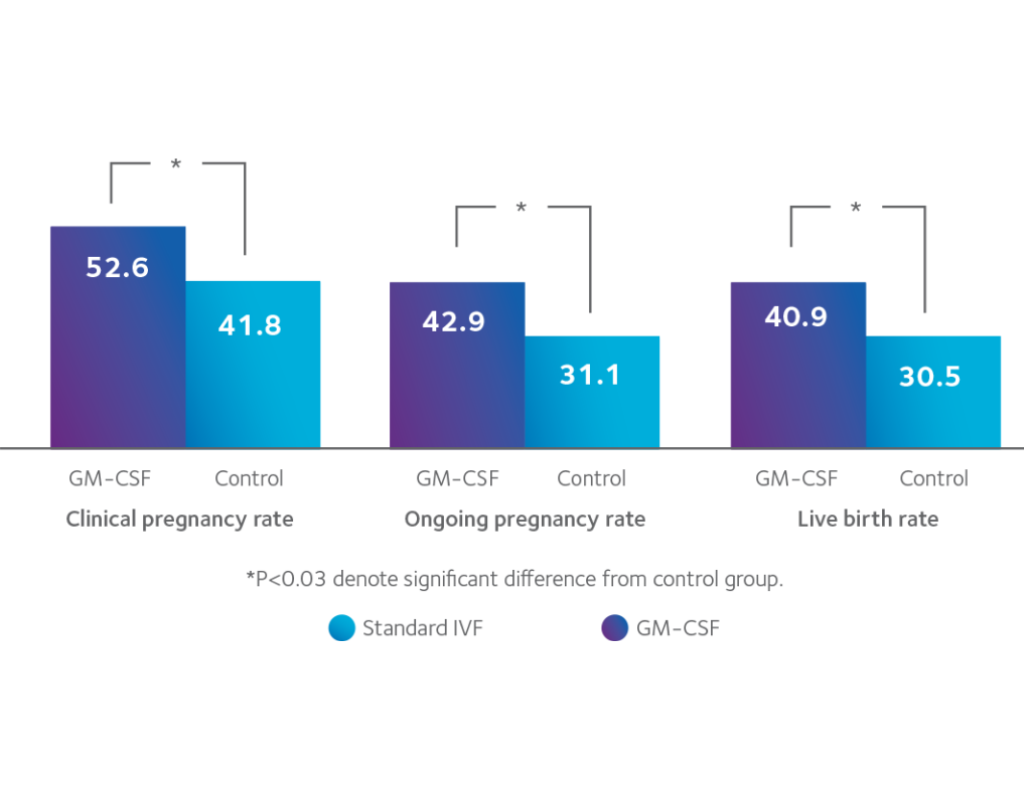
Who May Benefit from GM-CSF?
-
Women with a history of unsuccessful IVF/ICSI treatments
-
Patients with recurrent miscarriage
-
Patients with previou s failed embryo transfer cycles
-
Advanced maternal age patients
-
Patients undergoing frozen embryo transfer with poor-quality embryos