NEWS & KNOWLEDGE
Why Ovarian Stimulation Should Begin No Later Than Day 3 of the Menstrual Cycle

Why is it important to start ovarian stimulation no later than Day 3 of the menstrual cycle?
For women undergoing ovarian stimulation for egg freezing or assisted reproductive techniques such as IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) or ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection), hormone medications are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs simultaneously. These medications are typically administered for at least 8–12 days. Afterward, a trigger shot is given to induce ovulation approximately 34–36 hours before egg retrieval. The eggs are then collected either for freezing or for fertilization through ICSI.
Why must ovarian stimulation begin no later than Day 3 of the menstrual cycle?
Ovarian stimulation that begins on Day 2 or 3 of the menstrual cycle (with Day 1 being the first day of menstruation) is a standard and widely practiced protocol. At this time, the follicles are still in their early developmental phase. Stimulating the ovaries during this window allows for more uniform growth in both the size and number of developing follicles.
If stimulation starts after Day 3, the body may have already selected a dominant follicle to grow, while the remaining follicles begin to regress. This natural selection process can result in fewer mature eggs, reducing the efficiency and effectiveness of the stimulation cycle.
Benefits of initiating stimulation no later than Day 3
The use of hormonal medications helps stimulate all early-stage follicles to grow simultaneously. Initiating treatment by Day 3 ensures that the eggs grow at a similar rate, making it possible for the physician to retrieve eggs that are of similar maturity. This uniformity increases the chances of successful fertilization and development.
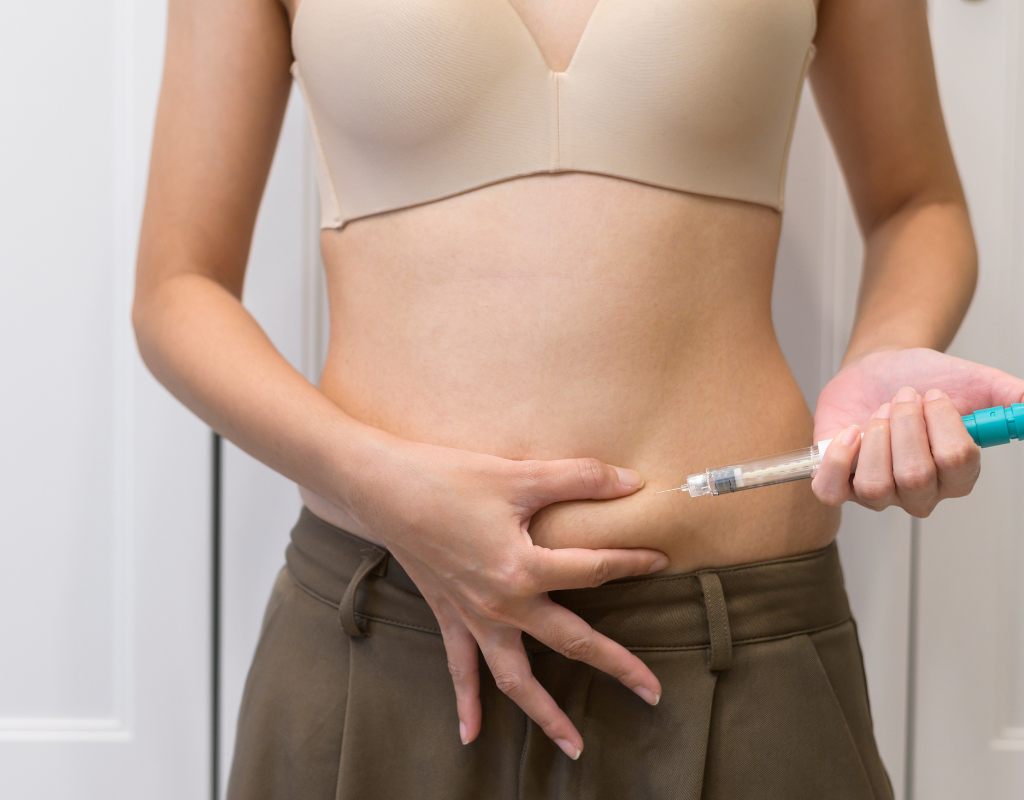
How to take care of yourself before starting ovarian stimulation
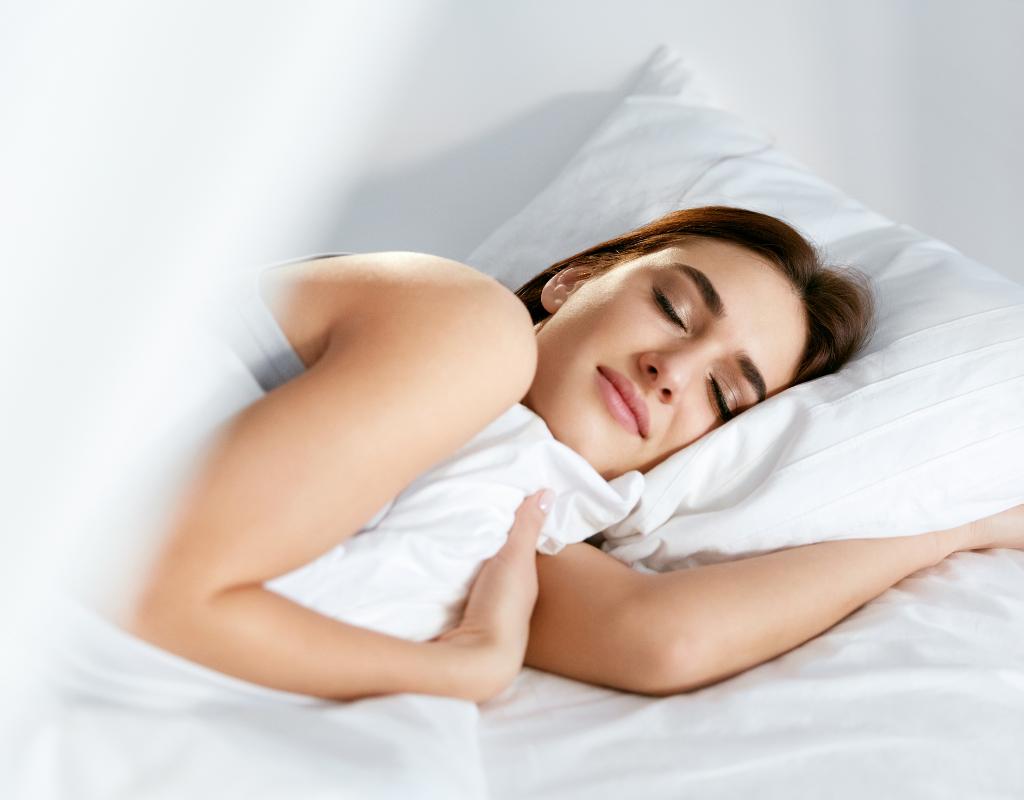
- Get adequate sleep
Rest is crucial during ovarian stimulation preparation. Sleeping 6–8 hours a night, especially going to bed before 10 p.m., helps the body’s systems and hormones function optimally.

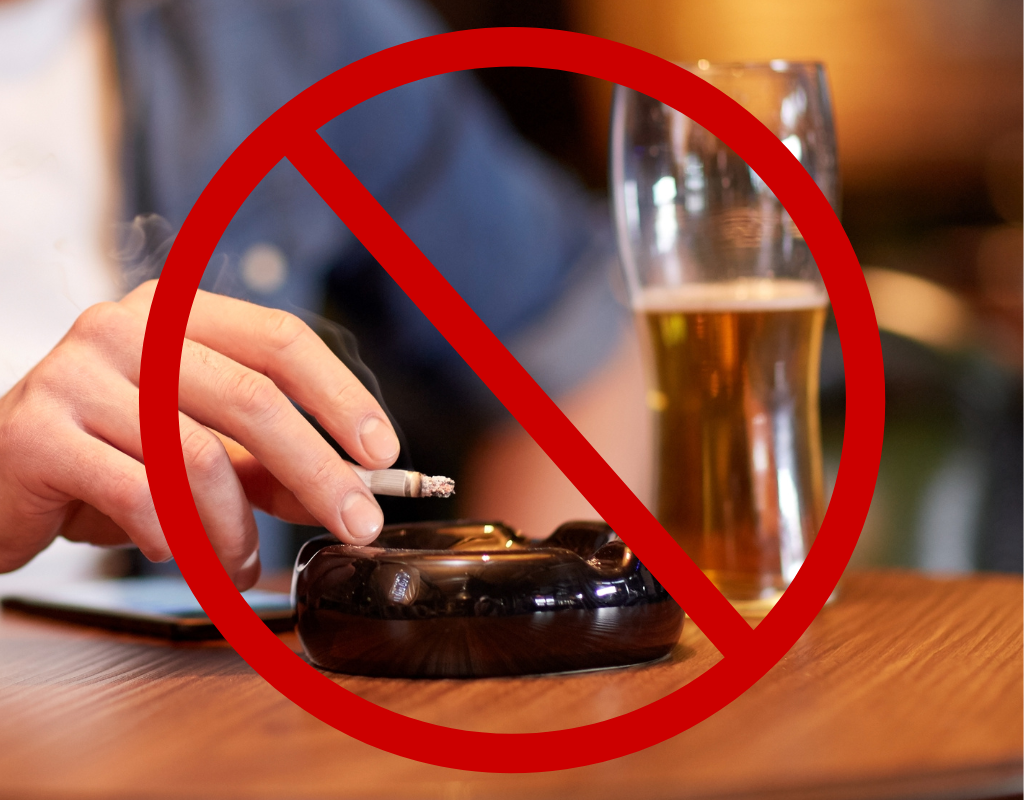
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
Harmful substances such as alcohol and tobacco can disrupt hormonal balance and interfere with ovarian function, affecting both egg development and ovulation.

- Reduce stress and maintain emotional well-being
Stress can trigger the release of cortisol, which may interfere with the body's hormone production and regulation. Managing stress through relaxation techniques is beneficial for hormonal health.

- Exercise appropriately
Engage in moderate exercise 2–3 times a week. Avoid strenuous activities such as intense abdominal workouts, heavy lifting, running, or jumping, as these can increase the risk of ovarian torsion, a potentially dangerous condition.

- Eat a balanced and nutritious diet
Consume a well-balanced diet that includes all five food groups. Focus on high protein intake approximately twice your body weight in grams per day. Include green leafy vegetables, fruits, and whole grains to support the body and improve egg quality.

By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert
For more information, please contact us via:
LINE Official : @nic_clinic or https://lin.ee/Mmq6m2K
Tel: 02-007-3973 or 095-370-2483


